In this tutorial, we'll discuss the various form* attributes for the HTML <input> element.
For example, an input field positioned outside of the HTML form structure will also work, if we specify the id of the form in the form attribute of that field (form="contact-form"), as you can see below.
<form action="/submission_page.php" id="contact-form">
<input type="text" name="fname" placeholder="First Name"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<input type="text" name="lname" placeholder="Last Name" form="contact-form">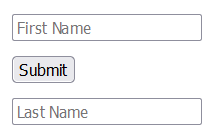
The "formaction" Attribute
The formaction attribute specifies the URL of the file that will handle the input when the form is submitted. It's important to note that this attribute takes precedence over the action attribute of the <form> element.
The formaction attribute is designed to work specifically with the submit and image input types.
<form action="/submission_page.php">
<input type="text" name="fname" placeholder="First Name"><br>
<input type="text" name="lname" placeholder="Last Name"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit1">
<input type="submit" formaction="/submission_page2.php" value="Submit2">
</form>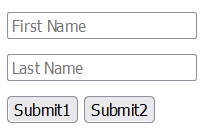
The "formenctype" Attribute
The formenctype attribute determines how form data should be encoded when submitted, applicable only to forms using the post method.
It's important to note that this attribute takes precedence over the enctype attribute of the <form> element.
The formenctype attribute is specifically designed for use with the submit and image input types.
<form action="/submission_page.php" method="post">
<input type="text" name="name" placeholder="First Name"><br>
<input type="file" name="picture" placeholder="Last Name"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
<input type="submit" formenctype="multipart/form-data"
value="Submit with Picture">
</form>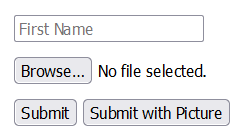
The "formmethod" Attribute
The formmethod attribute specifies the HTTP method used to send form data to the specified action URL.
It's important to note that this attribute takes precedence over the method attribute of the <form> element.
The formmethod attribute is intended for use with the submit and image input types.
Form data can be sent as URL variables (method="get") or as an HTTP POST transaction (method="post").
<form action="/submission_page.php" method="get">
<input type="text" name="fname" placeholder="First Name"><br>
<input type="text" name="lname" placeholder="Last Name"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit using GET">
<input type="submit" formmethod="post" value="Submit using POST">
</form>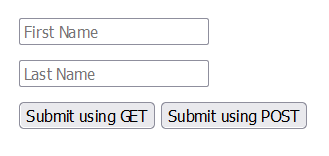
The "formtarget" Attribute
The formtarget attribute specifies a name or keyword indicating where to display the response received after submitting the form.
It's important to note that this attribute takes precedence over the target attribute of the <form> element.
The formtarget attribute is designed for use with the submit and image input types.
<form action="/submission_page.php">
<input type="text" name="fname" placeholder="First Name"><br>
<input type="text" name="lname" placeholder="Last Name"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
<input type="submit" formtarget="_blank" value="Submit (new window/tab)">
</form>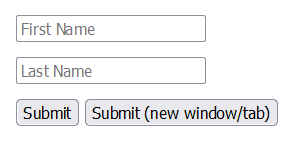
The "formnovalidate" Attribute
The formnovalidate attribute indicates that an <input> element should not undergo validation upon submission.
This attribute takes precedence over the target attribute of the <form> element.
The formnovalidate attribute functions exclusively with the submit input type.
<form action="/submission_page.php">
<input type="email" name="email" placeholder="Email"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
<input type="submit" formnovalidate="formnovalidate"
value="Submit (no validation)">
</form>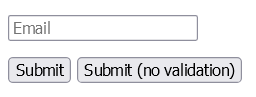
The "novalidate" Attribute
The novalidate attribute is used within a <form> element.
When included, novalidate indicates that the form data should not undergo validation upon submission.
<form action="/submission_page.php" novalidate>
<input type="email" name="email" placeholder="Email"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>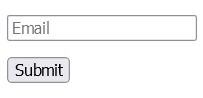
Please check below options for the links to our previous or next tutorial.
