A CSS animation allows an element to smoothly transition from one style to another.
You can modify as many CSS properties as you'd like, and do so multiple times.
You can animate HTML elements using CSS without the need for JavaScript!
How to use
To create a CSS animation, you need to define keyframes that specify the element's styles at different points in time.
In this tutorial, you'll learn about these animation properties:
@keyframesanimation-nameanimation-durationanimation-delayanimation-iteration-countanimation-directionanimation-timing-functionanimation-fill-modeanimation
The @keyframes Rule
When you define CSS styles within the @keyframes rule, the animation will smoothly transition from the existing style to the new style at specified moments.
To activate the animation, you need to link it to an element.
In the example below, the demo animation is applied to a <div> element. Over the course of 5 seconds, the animation will gradually shift the background color of the <div> element from red to green:
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
animation-name: demo;
animation-duration: 5s;
}
@keyframes demo {
from {background-color: red;}
to {background-color: green;}
}
In the example above, we defined the style changes using the keywords from and to, which correspond to 0% (start) and 100% (end) of the animation.
You can also use percentages to specify when style changes occur, allowing for multiple transitions throughout the animation.
Animation Duration
The animation-duration property determines the length of time an animation takes to complete. If animation-duration isn't set, the animation won't run, as its default value is 0s (0 seconds).
In the following example, the background color of the <div> element changes at 25%, 50%, and 100% of the animation duration:
div {
background-color: red;
animation-name: demo;
animation-duration: 2s;
}
@keyframes demo {
0% {background-color: red;}
25% {background-color: green;}
50% {background-color: blue;}
100% {background-color: orange;}
}
In the example below, both the background color and the position of the <div> element will change at 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100% completion of the animation:
div {
background-color: red;
position: relative;
animation-name: demo;
animation-duration: 5s;
}
@keyframes demo {
0% {background-color:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
25% {background-color:green; left:100px; top:0px;}
50% {background-color:blue; left:100px; top:100px;}
75% {background-color:orange; left:0px; top:100px;}
100% {background-color:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
Delay an Animation
The animation-delay property sets a delay before an animation begins.
In the example below, there is a 2-second delay before the animation starts:
div {
background-color: red;
animation-name: demo;
animation-duration: 5s;
animation-delay: 2s;
}
@keyframes demo {
from {background-color: red;}
to {background-color: green;}
}
Negative values can also be used with animation-delay. When a negative value is set, the animation begins as if it has already been running for that many seconds.
In the example below, the animation starts as though it has already been playing for 2 seconds:
div {
background-color: red;
animation-name: demo;
animation-duration: 5s;
animation-delay: -2s;
}
@keyframes demo {
from {background-color: red;}
to {background-color: green;}
}
Controlling Animation Repetitions
The animation-iteration-count property determines how many times an animation will run.
In the example below, the animation will repeat 2 times before stopping:
div {
background-color: red;
animation-name: demo;
animation-duration: 5s;
animation-iteration-count: 2;
}
@keyframes demo {
0% {background-color:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
50% {background-color:green; left:100px; top:0px;}
100% {background-color:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
The example below uses the value infinite to make the animation run endlessly:
div {
background-color: red;
animation-name: demo;
animation-duration: 5s;
animation-iteration-count: infinite;
}
@keyframes demo {
0% {background-color:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
50% {background-color:green; left:100px; top:0px;}
100% {background-color:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
Animation Direction
The animation-direction property controls whether an animation plays forwards, backwards, or alternates between the two.
The possible values for animation-direction are:
normal:The animation plays forwards (default).reverse:The animation plays backwards.alternate:The animation plays forwards first, then backwards.alternate-reverse:The animation plays backwards first, then forwards.
In the example below, the animation runs in reverse (backwards):
div {
background-color: red;
animation-name: demo;
animation-duration: 5s;
animation-direction: reverse;
}
@keyframes demo {
0% {background-color:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
50% {background-color:green; left:100px; top:0px;}
100% {background-color:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
The example below uses the value alternate to make the animation run forwards initially, then backwards:
div {
background-color: red;
animation-name: demo;
animation-duration: 4s;
animation-iteration-count: 2;
animation-direction: alternate;
}
@keyframes demo {
0% {background-color:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
50% {background-color:green; left:100px; top:0px;}
100% {background-color:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
In the example below, the value alternate-reverse is used to make the animation run backwards first, then forwards:
div {
background-color: red;
animation-name: demo;
animation-duration: 4s;
animation-iteration-count: 3;
animation-direction: alternate-reverse;
}
@keyframes demo {
0% {background-color:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
50% {background-color:green; left:100px; top:0px;}
100% {background-color:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
Defining Animation Speed Curves
The animation-timing-function property controls the speed curve of an animation.
Here are the possible values for animation-timing-function:
ease:Starts slow, speeds up, then slows down (default).linear:Maintains a consistent speed from start to finish.ease-in:Begins slowly.ease-out:Ends slowly.ease-in-out:Starts and ends slowly.cubic-bezier(n,n,n,n):Allows custom speed curves using thecubic-bezier function.
The example below demonstrates various speed curves that can be applied:
.div-one {animation-timing-function: linear;}
.div-two {animation-timing-function: ease;}
.div-three {animation-timing-function: ease-in;}
.div-four {animation-timing-function: ease-out;}
.div-five {animation-timing-function: ease-in-out;}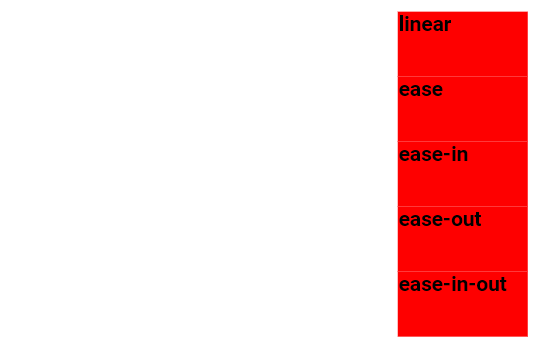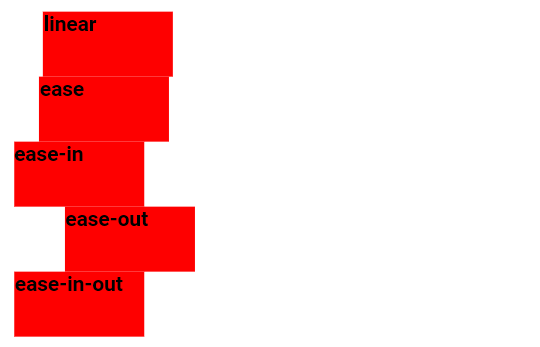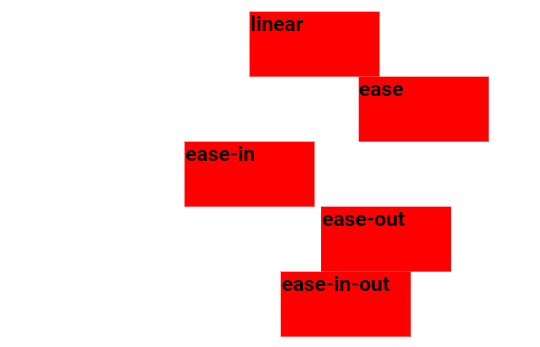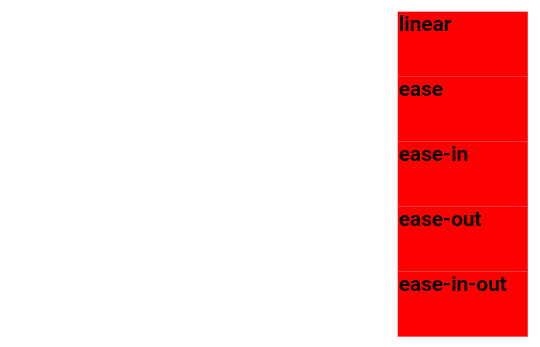
Controlling Styles Before and After Animation
By default, CSS animations don't apply styles to an element before the first keyframe or after the last keyframe. The animation-fill-mode property can change this behavior.
Here are the possible values for animation-fill-mode:
none:Default. The element won't retain any styles before or after the animation.forwards:The element keeps the style values from the last keyframe after the animation ends (affected byanimation-directionandanimation-iteration-count).backwards:The element applies the style values from the first keyframe during the animation delay period (affected byanimation-direction).both:The element retains styles in both directions, before and after the animation.
In the example below, the <div> element retains the style values from the last keyframe once the animation ends:
div {
background: red;
animation-name: demo;
animation-duration: 3s;
animation-fill-mode: forwards;
}
@keyframes demo {
from {background-color: red;}
to {background-color: green;}
}
In the example below, the <div> element applies the style values from the first keyframe before the animation starts, during the animation delay period:
div {
background: red;
animation-name: demo;
animation-duration: 3s;
animation-delay: 2s;
animation-fill-mode: backwards;
}
@keyframes demo {
from {background-color: red;}
to {background-color: green;}
}
In the example below, the <div> element applies the style values from the first keyframe before the animation begins and retains the style values from the last keyframe after the animation ends:
div {
background: red;
animation-name: demo;
animation-duration: 3s;
animation-delay: 2s;
animation-fill-mode: both;
}
@keyframes demo {
from {background-color: red;}
to {background-color: green;}
}
Animation Shorthand Property
The example below demonstrates the use of six different animation properties:
div {
animation-name: demo;
animation-duration: 5s;
animation-timing-function: linear;
animation-delay: 3s;
animation-iteration-count: infinite;
animation-direction: alternate;
}You can achieve the same animation effect as above by using the shorthand animation property:
div {
animation: demo 5s linear 3s infinite alternate;
}