In this tutorial, we'll discuss various HTML form elements.
The HTML <form> element can include any combination of the following form elements.
<form> - Creates an HTML form for user input.
<input> - Represents an input control.
<label> - Associates a label with an <input> element.
<select - Defines a drop-down list.
<textarea> - Represents a multiline input field (text area).
<button> - Creates a clickable button.
<fieldset> - Groups related elements within a form.
<legend> - Provides a caption for a <fieldset> element.
<datalist> - Defines a list of pre-defined options for input controls.
<output> - Displays the result of a calculation.
<option> - Represents an option within a drop-down list.
<optgroup> - Categorizes related options within a drop-down list.
The Input Element
One of the most commonly used form elements is the <input> element, which can be rendered in different ways based on the specified type attribute. For example, in case of text fields, we have:
<form>
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname">
</form>The Label Element
The <label> element is used to define a label for various form elements. This element is particularly beneficial for screen-reader users, as it allows the screen-reader to read the label aloud when the user focuses on the corresponding input element.
Additionally, users can just click on the text inside the <label> element to toggle the associated radio button or checkbox elements, which makes them easier to use.
To link a <label> element with an <input> element, the for attribute of the <label> tag should match the id attribute of the <input> element.
<form>
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br>
</form>The Select Element
The <select> element creates a dropdown list.
<label for="colors">Color:</label>
<select id="colors" name="colors">
<option value="white">white</option>
<option value="green">green</option>
<option value="blue">blue</option>
<option value="red">red</option>
</select>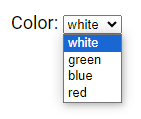
The <option> element represents an option that can be selected in a dropdown list.
By default, the first item in the dropdown list is selected.
To specify a pre-selected option, add the selected attribute to the <option> tag.
<label for="colors">Color:</label>
<select id="colors" name="colors">
<option value="white">white</option>
<option value="green"selected>green</option>
<option value="blue">blue</option>
<option value="red">red</option>
</select>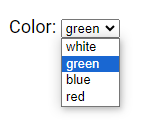
The Select Element - Visible Values
The size attribute is used to determine the number of visible options in a dropdown list.
<label for="colors" >Color:</label>
<select id="colors" name="colors" size="3">
<option value="white">white</option>
<option value="green">green</option>
<option value="blue">blue</option>
<option value="red">red</option>
</select>
The Select Element - Multiple Selections
The multiple attribute enables users to select multiple values from a dropdown list.
<label for="colors" >Color:</label>
<select id="colors" name="colors" size="4" multiple >
<option value="white">white</option>
<option value="green">green</option>
<option value="blue">blue</option>
<option value="red">red</option>
</select>
The Textarea Element
The <textarea> element creates a multi-line input field, also known as a text area.
<textarea name="message" rows="10" cols="30">
This is a text in the textarea.
</textarea>The rows attribute determines the visible number of lines in a text area.
The cols attribute specifies the visible width of the text area.
The size of the text area can also be specified using CSS.
<textarea name="message" style="width:250px; height:200px;" rows="10" cols="30">
The size of the text area can also be specified using CSS.
</textarea>The Button Element
The <button> element creates a clickable button.
<button type="button" onclick="alert('Button Example!')">Click here!</button>It's important to always specify the type attribute for the <button> element. Different browsers may use different default types for the <button> element.
The Fieldset and Legend Elements
The <fieldset> element is employed to group related data within a form.
The <legend> element, when nested within a <fieldset>, provides a caption for the group of related elements.
<form action="/submission_page.php">
<fieldset>
<legend>Personal:</legend>
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" value="John"><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname" value="Doe"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</fieldset>
</form>The Datalist Element
The <datalist> element defines a list of predefined options for an <input> element.
As users input data, they will see a dropdown list of the predefined options.
To associate the <input> element with the <datalist> element, use the list attribute in the <input> element and set it to the id of the <datalist> element.
<form action="/submission_page.php">
<input list="fruits">
<datalist id="fruits">
<option value="Apple">
<option value="Mango">
<option value="Orange">
<option value="Banana">
<option value="Peach">
</datalist>
</form>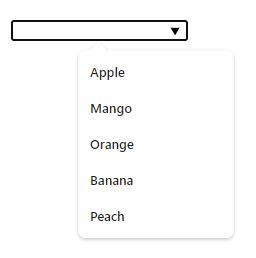
The Output Element
The <output> element is used to display the result of a calculation, such as one carried out by a script.
<form action="/submission_page.php"
oninput="x.value=parseInt(a.value)+parseInt(b.value)">
<input type="number" id="a" name="a" value="20">
<input type="number" id="b" name="b" value="20">
=
<output name="x" for="a b"></output>
<br><br>
<input type="submit">
</form>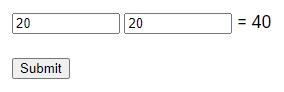
Please check below options for the links to our previous or next tutorial.
