HTML includes various elements for specifying user input and computer code. For example:
<code>
x = 5;
y = 6;
z = x + y;
</code>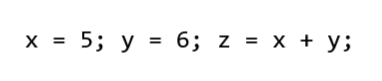
HTML <kbd> Element
The HTML <kbd> element is employed to indicate keyboard input. The content within is rendered in the browser's default monospace font.
<p>Download the webpage by pressing <kbd>Ctrl + S</kbd></p> 
HTML <samp> Element
The HTML <samp> element is utilized to denote sample output from a computer program. The content inside is displayed in the browser's default monospace font.
<p>Output from Program A:</p>
<p><samp>Processing complete!<br>Press any key to continue</samp></p> 
HTML <code> Element
The HTML <code> element is used to define a piece of computer code. The content inside is displayed in the browser's default monospace font.
<code>
x = 5;
y = 6;
z = x + y;
</code> 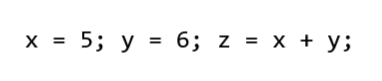
Note that the <code> element does not maintain additional whitespaces and line breaks.
To address this, enclose the <code> element within a <pre> element.
<pre>
<code>
x = 5;
y = 6;
z = x + y;
</code>
</pre> 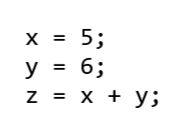
HTML <var> Element
The HTML <var> element is employed to define a variable in programming or a mathematical expression. The content inside is usually rendered in italics.
<p>The area of a rectangle is: <var>l</var> x <var>w</var>,
where <var>l</var> is the length, and <var>w</var> is the width.</p>
Please check below options for the links to our previous or next tutorial.
